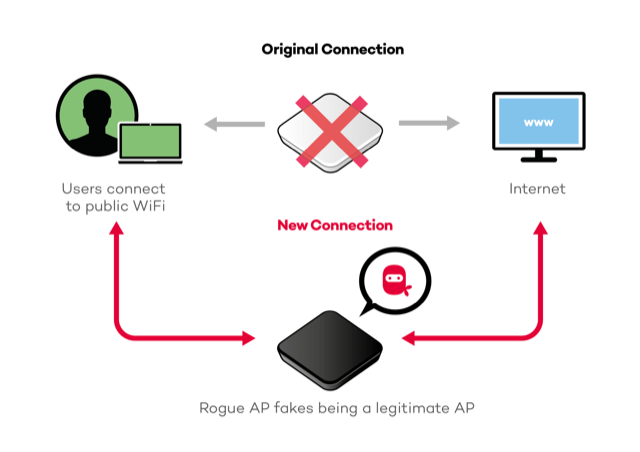
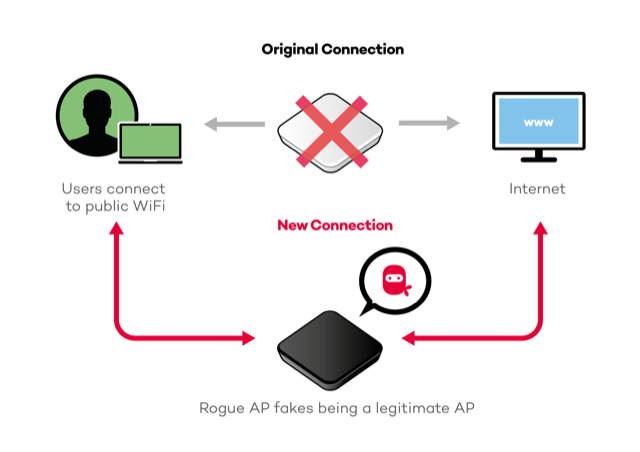
Cybersecurity is seen as one of the most important problems. In fact, wireless communication has inherent vulnerabilities as the signals share the electromagnetic spectrum. For network owners and system integrators, ensuring the secrecy and privacy of communications is a major concern when operating a WiFi network. Public networks with high user density, such as those present in convention centers, trains or airports, are the most vulnerable, as they are quite attractive for those who want to make malicious use of WiFi. The most common attacks such as Rogue AP or man-in-the-middle are very easy to carry out with free tools, and are the easiest to deceive unwary users.
A Rogue AP is a wireless access point able to fake one of the legitimate APs on your network. It does so by either cloning the SSID announced by your teams, the MAC address of one of them (BSSID), or even the Beacon frames and web applications used (especially critical with captive portals). These Rogue APs are deployed instantly by people who want your users’ devices to connect to them, thus allowing access to sensitive data (from user login and password, to credit cards).
In this context, Galgus has developed and patented Cognitive HotspotTM Technology (CHT), an embedded software that is installed within APs of a wide range of manufacturers to provide them with advanced features. CHT has modules to optimize the network, to reduce energy consumption or to locate devices, but also has modules to detect and mitigate the outbreak of cybersecurity problems such as Rogue APs.
Discover Galgus’ solution to cybersecurity in WiFi networks here!