The rise of Wi-Fi technology in the latest years has been remarkable. It has become one of the most widely spread communication systems together with celular networks.
The increasing need for greater data flow that is demanded in the world alongside the advances proposed by the scientific society and implemented by the industry have caused the digital revolution that we are experiencing today, in which Wi-Fi networks play a key role.
The mass deployment of this technology in the world has led to the search for its use as interconnection of devices but also – going one step further – as a base for other interesting purposes. Among them, data analytics stands out.
In recent years, the digital revolution that is being experienced and, that we have commented on, has evolved into the so-called “Data Revolution”. This is due to the growth in the amount of data that each person generates. which is possible to obtain thanks to the technologies that surround us. And Wi-Fi networks are no exception.
In this article we are going to explore the latest Wi-Fi technology trends, and therefore, be able anticipate the developments and changes that will come in 2024.
Wi-Fi technology development

The implementation of the latest local wireless network standard, Wi-Fi 6, based on the IEEE 802.11ax standard, has been successful, thanks to its spectral compatibility with previous versions.
However, in 2022 and 2023 the spot has been on Wi-Fi 6E (enhaced): this is the improved version of the standard, whose main change has been the inclusion of the 6 GHz band. Previously, the operating bands of Wi-Fi networks were focused on two: 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz.
All in all, it can be sum up that “the higher the operating frequency, the higher the speed, but the lower the range.” Wi-Fi 6E proposes to expand the available spectrum by up to 1.2 GHz, reaching up to 7.125 GHz, being able to accommodate many more devices, thus freeing networks from congestion and further increasing transmission speeds and reducing latency.
As accessing to the different frequency bands is regulated by the government institutions of each country, in the last years the different communications committees have worked to decide which bands to adopt.
For instance, in the US, the entire 6 GHz band was deployed, while Europe decided to reach half of the band, a maximum of 6’425 GHz. All these have been possible by Wi-Fi 6E which has open the way for the true revolution that will begin in 2024: the IEEE 802.11be standard, which will be known as Wi-Fi 7.
This new standard will operate in the already known frequency bands (2.4 GHz, 5GHz and 6GHz), but will provide improvements that will unleash the true potential of these frequencies: firstly, new operating channels twice as wide as in Wi-Fi. Fi 6 (up to 320 MHz) with modulations of up to 4K QAM, which will result in transmission speeds (peak) of up to 5.8Gbps.
On the other hand, MLO (Multi-Link Operation) technology will allow the same device to simultaneously combine different channels from different frequency bands, and can also reduce latency to tens of milliseconds. All of this will allow applications such as 4K and 8K video streaming, cloud-gaming and video conferencing to reach levels of quality never seen before.
2024 will be the year of implementation of this new standard. With an estimated 84 million Wi-Fi 7 devices shipping by 2024, Wi-Fi 7 will soon usher in the next generation of Wi-Fi.
Wi-Fi and the Internet of Things (IoT)

It’s worldwide kwnon the revolution caused by the so-called “Internet of things (IoT)” in our sector, as well as the key role of Wi-Fi networks in it.
From domestic devices such as CCTV cameras to industrial devices such as automated robots, through the wide world of smart cities, the interconnection of these devices (the paradigm called M2M, Machine to Machine) has been crucial and the latest Wi-Fi standards have responded to this demand in an exceptional way.
This has allowed the industry to take giant steps, not only through to advances in the versions of Wi-Fi 6 and Wi-Fi 6E, but with specific versions that solve cases where range is key, such as Wi-Fi Fi HaLow.
In 2024, the release of the 6GHz band is expected to catapult the implementation of IoT to another level. In fact, already in 2021 IoT devices surpassed smartphone sales and are expected to surpass all customer devices in 2027. The development of the new Wi-Fi 7 will be the launch point, and it will be joined by the already mentioned Wi-Fi HaLow and the recently launched Very Low Power (VLP) Wi-Fi.
AI en Wi-Fi
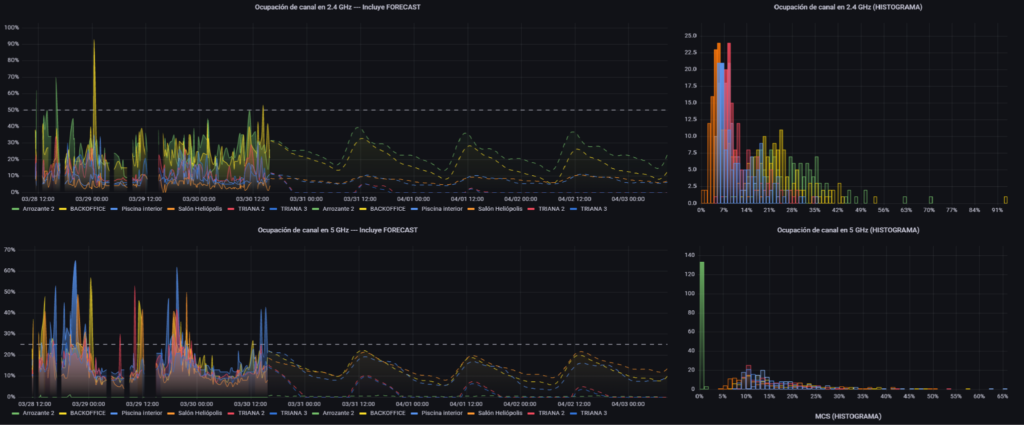
2023 is known as the year of settling and democratisation of a technology present in every conversation of any area in society: Artificial Intelligence (AI).
The achievements achieved by this revolution are undeniable, and the main advantage is its versatility. There are many fields of application where AI can play a crucial role, and for it to achieve its greatest splendor what it needs is data. Many data. Therefore, it is trivial to admit that in the Wi-Fi networks of the future, AI is going to have a lot to say.
Communications networks are increasingly complex and heterogeneous, with an infrastructure with numerous different devices and a multitude of users. This causes countless logical and physical problems that require system integrators to be experts in configuration and diagnosis in order to resolve them in a short time.
In recent years, the scientific community has researched about it: the application of Big Data and AI in Wi-Fi analytics for network optimisation. In this regard, Galgus has been a pioneer with its CHT (Cognitive Hotspot Technology) technology and has been working on the next step to measure the health of the network, spot possible anomalies and automate solutions, known as Network Health.
The trend shows that in 2024 these systems will gain a lot of visibility and importance, minimising failures or misconfigurations in the networks.
Location & Presence Analytics
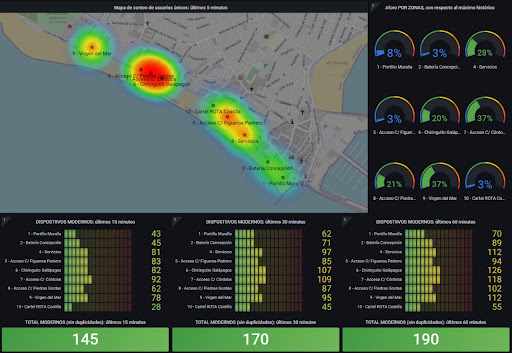
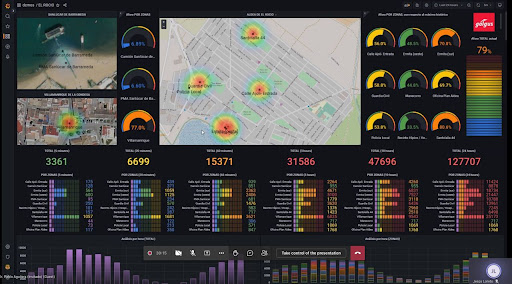
Indoor location and tracking has been one of the industry’s biggest issues in recent years. Many technologies have been developed, and achieve very good results, such as Bluetooth, Ultra Wide Band (UWB) or RFID.
However, all of these techs have the same issue: they require the installation of a specific infrastructure. To solve this problem, much progress has been made in the 802.11 standard lately.
Wi-Fi infrastructure allows the democratisation of access to location and presence analytics. Due to the many signals and data that Wi-Fi devices emit, it is possible to track and estimate the count and position of devices that pass through the vicinity of the network, without even needing to be connected to the network.
It’s this aspect where the most important innovations in Wi-Fi analytics are found. Specifically, Galgus has developed Galgus Presence & Location Analytics this last year, managing to provide counting information to spaces such as the Santa Cruz neighborhood in Seville, the Rota coastal area or the El Rocío pilgrimage.
In this regard, the scientific community has made great progress and in 2023 the new advanced localization standard 802.11az (Next Generation Positioning, NGP) was presented, which joins the family of localization proposals provided by 802.11mc.
It is therefore expected in 2024 that this new technology will begin to be deployed since with IEEE 802.11az, the location precision has gone from 2 meters to a submeter precision: even in the area of less than 0.1 meters.
This year, therefore, applications such as indoor navigation will become a reality, such as GPS in vehicles, which can guide you, for example, through a shopping center to indicate how to get to the desired store, or inside the store to reach the product you want.
5G and its interaction with Wi-Fi: Galgus Connect
The successful mass deployment that the new generation of 5G cellular networks has achieved in the last year will cause its interaction and integration with Wi-Fi networks to become a fact in 2024. Work has been done recently along this line, culminating in the development of Passpoint.
Passpoint is a standardized technology that pursues convergence between cellular networks (4G/5G) and Wi-Fi, allowing the seamless transition of users between both networks, who are authenticated using the credentials of their SIM card.
In this way, users do not have to do anything, simply enjoy the best quality of service at any times, dynamically adapting to the environment. This is a joint effort coordinated by the Wi-Fi Alliance (probably the largest by the Wi-Fi community to date).
Passpoint not only guarantees the dynamic and adaptive support of the Wi-Fi network to the 5G network when needed, but also allows the owner of the infrastructure to reach an agreement with telecommunications operators to monetise this “rent” of their access points that come to the aid.
To achieve this, it is crucial that the Wi-Fi network is able to provide continuous proof of being able to provide quality of service (QoS) to the users who will become dependent on it.
In this sense, Galgus Connect is the product that Galgus is building to facilitate the deployment, management and support of cellular + Wi-Fi convergence networks based on Passpoint, powered by CHT (Cognitive Hotspot Technology). This way, the Wi-Fi network continually ensures that performance, robustness and security requirements are met so that the 4G/5G network has confidence when transferring users to it.

In conclusion, the year 2024 will become a turning point in the evolution of Wi-Fi networks and data analytics. With the implementation of the innovative Wi-Fi 7 standard and the exponential growth of the Internet of Things, we will witness a qualitative leap in the quality, speed and range of wireless connections.
The integration of Artificial Intelligence into Wi-Fi network management promises unprecedented optimization, while new location technologies such as the IEEE 802.11az standard will open the door to advanced location applications such as indoor navigation.
These advances, along with the synergy between 5G and Wi-Fi networks, will not only improve the user experience, but will also drive a wave of innovation across multiple sectors, transforming our interaction with technology and the world around us.
At Galgus we will keep an eye on all these trends, as well as the new ones that will emerge over the next 12 months, so don’t miss out on this blog and our social media channels.
Sources:
- https://www.csic.es/es/actualidad-del-csic/la-revolucion-de-los-datos
- https://www.wi-fi.org/countries-enabling-wi-fi-in-6-ghz-wi-fi-6e
- https://www.wi-fi.org/beacon/the-beacon/wi-fi-7-advanced-connectivity-for-the-next-generation
- https://www.wi-fi.org/beacon/the-beacon/wi-fi-7-advanced-connectivity-for-the-next-generation
- https://www.networkworld.com/article/3688434/wi-fi-halow-wireless-for-the-internet-of-things.html
- https://www.idc.com/getdoc.jsp?containerId=prUS50563423
- https://docs.fcc.gov/public/attachments/DOC-397285A1.pdf
- https://standards.ieee.org/beyond-standards/newly-released-ieee-802-11az-standard-improving-wi-fi-location-accuracy-is-set-to-unleash-a-new-wave-of-innovation/
- https://www.wi-fi.org/discover-wi-fi/passpoint









